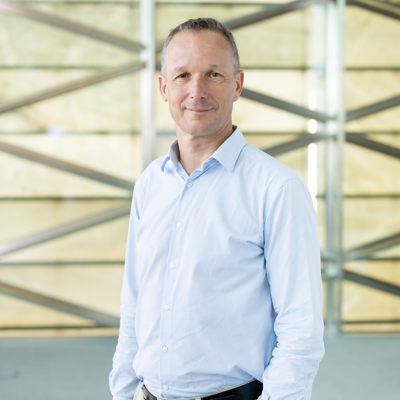
Paul Martin Mai
Professor, Earth Systems Science and Engineering
Physical Science and Engineering Division
“Understanding earthquake physics is critical for improved seismic hazardassessment and earthquake risk mitigation, to save lives and societies.”
Program Affiliations
Biography
Dr. Paul Martin Mai is a professor of geophysics in the Earth Systems Science and Engineering program of the Physical Sciences and Engineering Division at KAUST. He joined the university in 2009 as a founding faculty member, bringing expertise in earthquake physics, seismology and earthquake hazard. His research group, Computational Earthquake Seismology (CES), works on a range of topics related to earthquake system science, dynamics of earthquake rupture processes, ground-motion and tsunami simulations, and imaging Earth structure, often using supercomputers for simulations and imaging. Developing geothermal energy as an alternative green and sustainable resource in Saudi Arabia is another focus. Prior to KAUST, Professor Mai served as senior research scientist at the Institute of Geophysics at ETH Zürich (2004-2009). Additionally, he currently serves as the Editor-in-Chief of the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America (BSSA), and previously was the Seismology Division President of the European Geosciences Union (2015 to 2019). He has published over 150 peer-reviewed papers and supervised more than 50 graduate students (M.Sc. and Ph.D.) and 20 postdoctoral researchers.
Research Interests
Professor Paul Martin Mai’s research spans from fundamental earthquake physics toearthquake-engineering applications, examining multi-scale earthquake phenomena usingearthquake-source imaging, dynamic rupture modeling, and fault and earthquakemechanics. His work extends to strong ground-motion properties and high-performancecomputing-enabled physics-based seismic and tsunami simulations, including scattering inheterogeneous media. Another key research focus involves using seismic data to image thestructure of the Earth’s crust and upper mantle beneath the Arabian plate, with the goal tounderstand the geodynamics of the Arabian plate and Red Sea.
Education Profile
Postdoctoral Fellow, Institute ofGeophysics at ETH Zürich, 2002-2004
Ph.D., Earthquake Seismology,Stanford University, USA, 2001
M.Sc., Geophysics, University ofKarlsruhe, Germany,1995
B.Sc., Physics, University ofKarlsruhe, Germany,1991
Awards and Recognitions
Publications
Research Areas
- Earth Science and Engineering