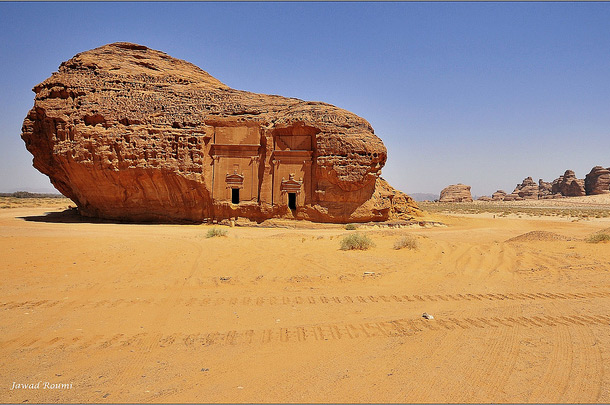
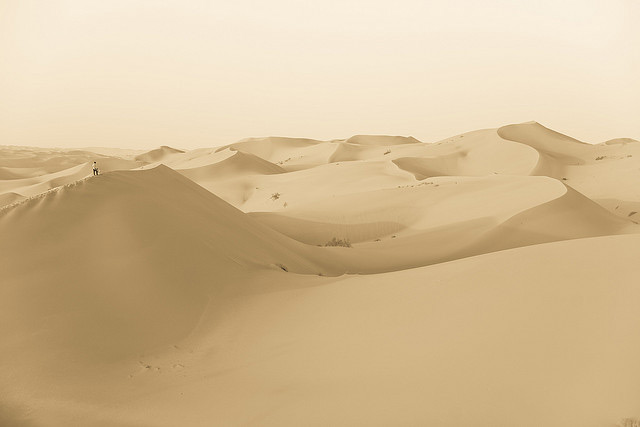
About Saudi Arabia
The Home of Islam is as diverse as it is surprising. It is a country with deep roots
in tradition yet one that is racing into the future. It is a land of astonishing natural
beauty ranging from the sculpted sand dunes of the Empty Quarter to the waters of the Red
Sea.
Capital: Riyadh
Land Size: 2.149,690 sq km / 829,999 sq miles
Language: Arabic, but English is widely used in business
Currency: Saudi Riyal (SR3.75 to the US$1.00)
Saudi Arabia's 2011 population is estimated to be about 26 million, including about 5.6 million resident foreigners. Some cities and oases have densities of more than 1,000 people per square kilometer (2,600 per sq. mi). The annual population growth rate for Saudi Arabia as of 2011, is 1.5%.
Saudi Arabia’s work force is 7.3 million strong with about 80% foreign workers (2010 est.); industry--21%; services (including government)--72%; agriculture—7%.
Saudi Arabia in Perspective
- Geography
- Major Cities
- Terrain
- Wildlife
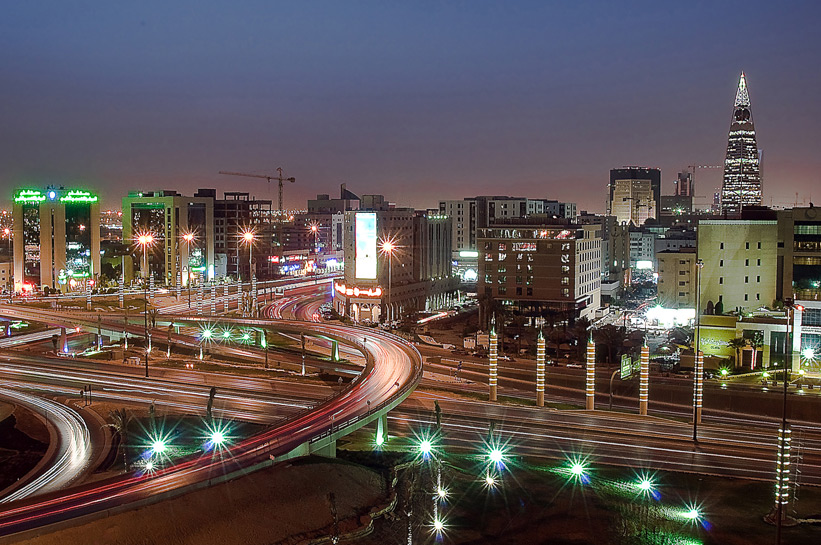

Saudi Arabia is the largest country in the Arabian
Peninsula. It occupies an area about the size of the
United States east of the Mississippi River.
Located in southwest Asia, at the crossroads of Europe, Asia and Africa; Saudi Arabia extends from the Red Sea in the west to the Arabian Gulf in the east. It’s land mass comprises slightly more than 80% of the Arabian Peninsula.
Bordered on the north by Jordan, Iraq and Kuwait, on the south, by Yemen and Oman, and on the east by the United Arab Emirates, Qatar and Bahrain; Saudi Arabia is a true crossroads between the East and West.
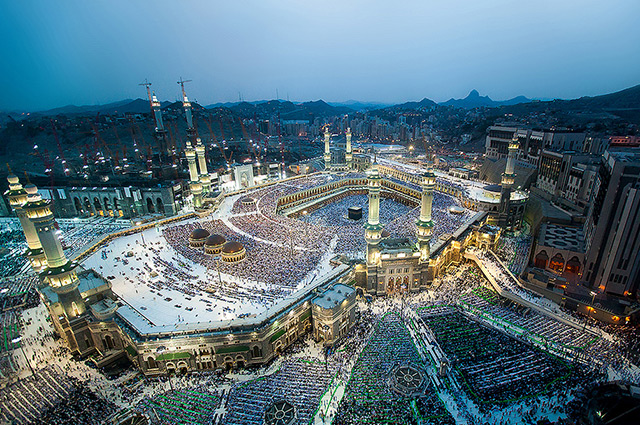

Islam’s holiest city, Makkah, is located in Saudi Arabia. Makkah is the birthplace of the Prophet Muhammad, the location of the Holy Kaaba, and the focal point of the Islamic Pilgrimage (Hajj).
Saudi Arabia’s capital is Riyadh, which lies in the central region. The oil boom initiated an era of growth in the city that continues to this day. The Kingdom’s increasingly important position in regional affairs is reflected in the choice of Riyadh for the headquarters of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC).
Jeddah is the second largest city after Riyadh, it is the main port of the Kingdom on the Red Sea and main gate through which most of the pilgrims to Makkah arrive by air and sea and just north of Jeddah is the village of Thuwal where the KAUST campus is located.
Known as the “World Energy Capital,” Dammam is the largest town in the eastern region. Located near Dammam are the most important centers in the world for the production and refining of petroleum.

Islam’s holiest city, Makkah, is located in Saudi Arabia. Makkah is the birthplace of the Prophet Muhammad, the location of the Holy Kaaba, and the focal point of the Islamic Pilgrimage (Hajj).
Saudi Arabia’s capital is Riyadh, which lies in the central region. The oil boom initiated an era of growth in the city that continues to this day. The Kingdom’s increasingly important position in regional affairs is reflected in the choice of Riyadh for the headquarters of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC).
Jeddah is the second largest city after Riyadh, it is the main port of the Kingdom on the Red Sea and main gate through which most of the pilgrims to Makkah arrive by air and sea and just north of Jeddah is the village of Thuwal where the KAUST campus is located.
Known as the “World Energy Capital,” Dammam is the largest town in the eastern region. Located near Dammam are the most important centers in the world for the production and refining of petroleum.
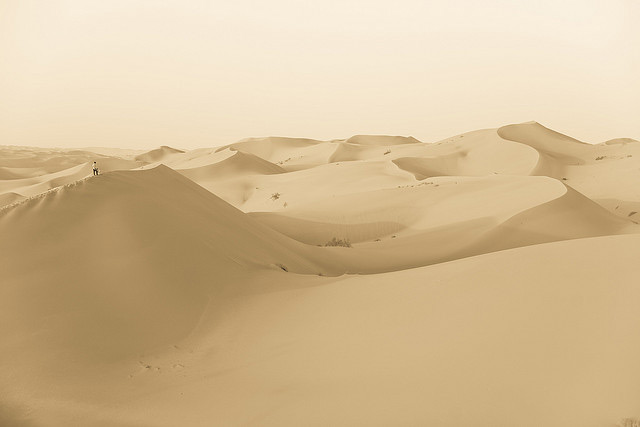

Saudi Arabia’s terrain could be described in one word: varied.

Saudi Arabia’s terrain could be described in one word: varied.
- The Coastland comprises the coastal plains and low hills bordering the Red Sea and the Arabian Gulf.
- The Harrat are regions covered by Cenozoic flood basalt forming flat areas of bouldery, incised terrain difficult to traverse.
- Sand Seas consist of large areas of wind-blown sand, the most famous of which, of course, is the Rub’ al Khali (the Empty Quarter).
- Mountains exist around the margin of the Arabian Peninsula, including those that rise up to the lip of the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden escarpment at elevations of 2000-3600 m.
- Much of the peninsula consists of vast regions of nearly flat plateaus and plains covered by weathered rock, sand, and gravel, that are interrupted by hills and ridges.

Islamic teachings affirm the need to conserve areas for purposes pertaining to the common good. These areas are called hima, which means "protected area" or "reserve." Some traditional himas in Saudi Arabia have been managed sustainably since early Islamic times, and are among the most long-standing examples of rangeland and woodlands conservation known.
At present, the Kingdom has 15 protected areas established by the National Commission for Wildlife Conservation and Protection (NCWCP). Additionally, the NCWCP has reintroduced a number of species to the Kingdom including the Arabian Oryx and the Houbara Bustard.
It is not uncommon to see baboons in some areas of Saudi Arabia. Baboon numbers used to be partially controlled by their natural predators, leopard and striped hyena but these have been hunted over many years and are no longer seen in the region.
According to the present estimates, Saudi Arabia contains 70 species (3%) of trees, 600 species (27%) of shrubs, and about 1583 (70%) species of herbs.

Islamic teachings affirm the need to conserve areas for purposes pertaining to the common good. These areas are called hima, which means "protected area" or "reserve." Some traditional himas in Saudi Arabia have been managed sustainably since early Islamic times, and are among the most long-standing examples of rangeland and woodlands conservation known.
At present, the Kingdom has 15 protected areas established by the National Commission for Wildlife Conservation and Protection (NCWCP). Additionally, the NCWCP has reintroduced a number of species to the Kingdom including the Arabian Oryx and the Houbara Bustard.
It is not uncommon to see baboons in some areas of Saudi Arabia. Baboon numbers used to be partially controlled by their natural predators, leopard and striped hyena but these have been hunted over many years and are no longer seen in the region.
According to the present estimates, Saudi Arabia contains 70 species (3%) of trees, 600 species (27%) of shrubs, and about 1583 (70%) species of herbs.